National Green Tribunal (NGT)
Context:
- Supreme Court has held in a judgment recently that NGT is a “unique” institution established for enforcement of environmental rights protected under the Right to Life and the Parliament has not excessively delegate power to the Centre by authorising it to establish the National Green Tribunal.
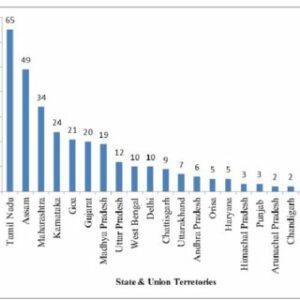
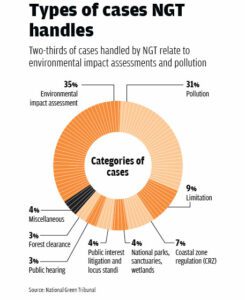

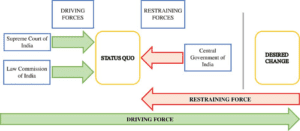
About NGT:
- It is a specialised body established under the National Green Tribunal Act (2010) for the effective and timely resolution of matters involving environmental protection and forest and other natural resource conservation.
- India became the third country in the world, after Australia and New Zealand, to establish a specialised environmental tribunal, and the first developing country to do so with the founding of the NGT.
- The NGT is required to decide on petitions or appeals within six months of their filing.
- The Tribunal is not bound by the procedure laid down under the Code of Civil Procedure 1908, but shall be guided by principles of ‘natural justice’.
Composition:
- The Chairperson, Judicial Members, and Expert Members make up the Tribunal. They are appointed for a five-year term and are not eligible for reappointment.
- The Central Government, in collaboration with the Chief Justice of India, appoints the Chairperson (CJI).
- The Union government will appoint a Selection Committee to appoint the Judicial and Expert Members.
- The tribunal must have at least 10 and no more than 20 full-time judicial and expert members.
Challenges:
- The NGT does not have jurisdiction over the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 or the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act of 2006. This limits the NGT’s authority and, at times, makes it difficult for it to function, as the fundamental issue of forest rights is inextricably related to the environment.
- Under Article 226 (authority of High Courts to issue certain writs), the NGT’s judgements are being contested in various High Courts, with several claiming that a High Court has superiority over the NGT.
Source: THE HINDU.
For more update, click here to join our telegram channel




